728x90
그래프와 인접 행렬
🔍 무방향 그래프
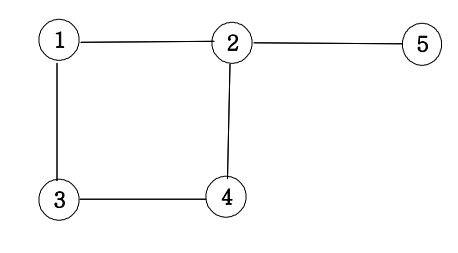
📌 무방향 그래프의 인접행렬 만들기
public class Prac {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int N = 5; // 정점 개수
int L = 5; // 간선 개수
// 정점의 데이터가 1부터 시작
int[][] arr = new int[N+1][N+1];
arr[1][2] = arr[2][1] = 1;
arr[1][3] = arr[3][1] = 1;
arr[2][4] = arr[4][2] = 1;
arr[3][4] = arr[4][4] = 1;
arr[2][5] = arr[5][2] = 1;
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
for(int k=1; k<N+1; k++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][k]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}01100
10011
10010
01010
01000
📌 정리
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Prac {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = 5; // 정점 개수
int L = 5; // 간선 개수
int[][] arr = new int[N][N];
for(int i=0; i<L; i++) {
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
arr[from][to] = arr[to][from] = 1;
}
}
}
🔍 방향 그래프
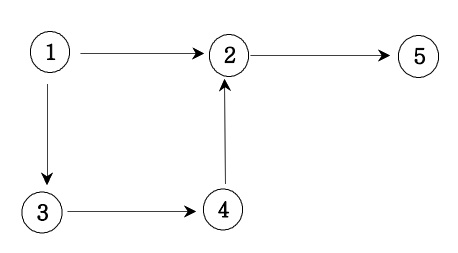
📌 방향 그래프의 인접행렬 만들기
public class Prac {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int N = 5; // 정점 개수
int L = 5; // 간선 개수
// 정점의 데이터가 1부터 시작
int[][] arr = new int[N+1][N+1];
arr[1][2] = 1;
arr[1][3] = 1;
arr[3][4] = 1;
arr[4][2] = 1;
arr[2][5] = 1;
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
for(int k=1; k<N+1; k++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][k]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}01100
00001
00010
01000
00000
📌 정리
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Prac {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = 5; // 정점 개수
int L = 5; // 간선 개수
int[][] arr = new int[N][N];
for(int i=0; i<L; i++) {
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
arr[from][to] = 1;
}
}
}
🔍 가중치 방향 그래프
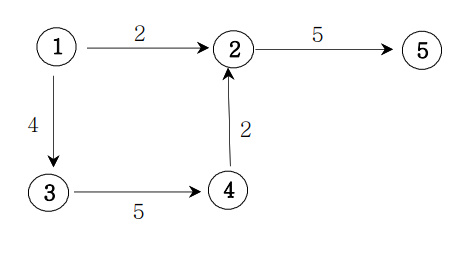
📌 가중치 방향 그래프의 인접행렬 만들기
public class Prac {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int N = 5; // 정점 개수
int L = 5; // 간선 개수
// 정점의 데이터가 1부터 시작
int[][] arr = new int[N+1][N+1];
arr[1][2] = 2;
arr[1][3] = 4;
arr[3][4] = 5;
arr[4][2] = 2;
arr[2][5] = 5;
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
for(int k=1; k<N+1; k++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][k]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}02400
00005
00050
02000
00000
📌 정리
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Prac {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = 5; // 정점 개수
int L = 5; // 간선 개수
int[][] arr = new int[N][N];
for(int i=0; i<L; i++) {
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
int score = sc.nextInt(); // 가중치
arr[from][to] = score;
}
}
}
🔍 경로 탐색 문제
주어진 방향 그래프에서 1번 정점에서 5번 정점으로 가는 모든 경로의 가지 수를 출력하도록 하시오.
입력 설명
- 첫번째 줄에는 정점의 수 N(1<=N<=20)와 간선의 수 M이 주어진다.
- 그 다음부터 M줄에 걸쳐 연결정보가 주어진다.
출력설명
- 총 가지수를 출력한다.
📍 테스트 케이스 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
입력 예제
5 9
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 1
2 3
2 5
3 4
4 2
4 5
출력 예제
6
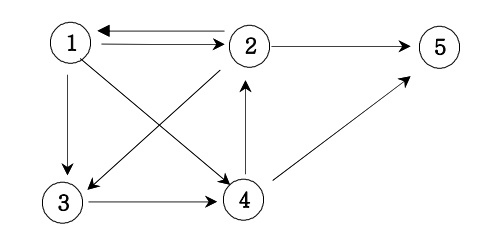
📌 코드 구현
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Solution {
static int[][] graph;
static boolean[] check;
static int N, M, count, start, end;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt(); // 정점 수
M = sc.nextInt(); // 간선 수
graph= new int[N+1][N+1];
check = new boolean[N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=M; i++) {
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
graph[from][to] = 1;
}
start = 1;
end = 5;
check[start] = true;
DFS(start);
System.out.println(count);
}
static void DFS(int start) {
if(start == end) {
count++;
return;
}
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
if(graph[start][i]==1 && !check[i]) {
check[i] = true;
DFS(i);
check[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
728x90
'[알고리즘] > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 그래프 최단거리 (BFS) (0) | 2022.03.01 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조]그래프와 인접 리스트 (0) | 2022.03.01 |
| [자료구조] 이진 트리 레벨 탐색 (BFS : Breath-First-Search) (0) | 2022.02.22 |
| [자료구조] 순열 (0) | 2022.02.17 |
| [자료구조] 부분 집합 구하기 (DFS) (0) | 2022.02.16 |
![[자료구조] 그래프와 인접행렬](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FOIG21%2Fbtrt4gA2mFi%2FSaIUw8mW4KwBCc14sxvvgk%2Fimg.jpg)